Trainer makers compete; many aircraft take first flights
December 2016
The Aircraft Design Technical Committee promotes optimization of aircraft systems, including analysis of their future potential.
The year was busy for aircraft development across many sectors of the industry. The U.S. Air Force’s T-X advanced pilot trainer has multiple manufacturers competing. Lockheed Martin, along with Korea Aerospace Industries, is upgrading the T-50. Raytheon’s T-100 entrant is a development of Leonardo-Finmeccanica’s M-346. There were also two new entrants. Northrop Grumman, BAE Systems and L-3 revealed a prototype (built by Scaled Composites) in August, and the Boeing/Saab team rolled out not one, but two airframes Sept. 13. Other military programs of note included China’s large four-engine airlifter, the Avic Y-20, entering service. Boeing’s KC-46 continued flight testing that led to award of low-rate initial production. The U.S. Air Force declared the F-35A basic combat-ready in August.
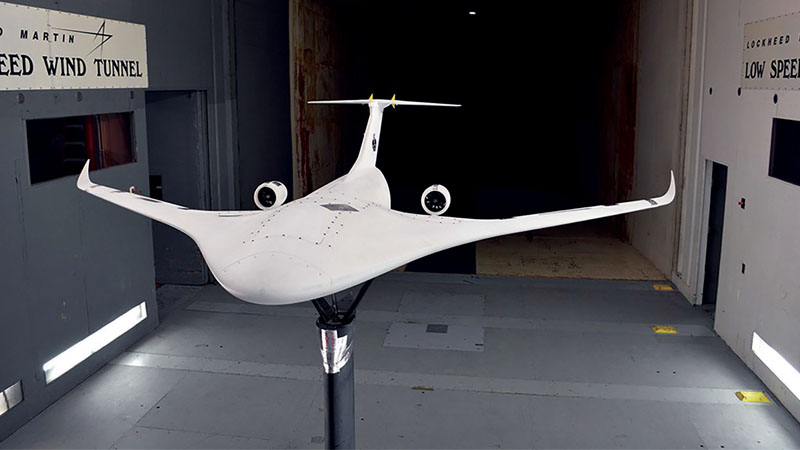
Numerous advanced technology initiatives made progress. Japan’s X-2 stealth technology demonstrator achieved first flight in April. South Korea launched a five-year technology demonstrator program for unmanned strike aircraft. DARPA’s vertical takeoff and landing experimental plane, or VTOL X-plane, efforts continued, with Virginia-based Aurora Flight Sciences granted development of the LightningStrike, a tilt-wing, distributed hybrid electric propulsion vehicle targeting high-speed and VTOL capabilities. Northrop Grumman commenced wind tunnel testing of its tail-sitting VTOL concept for DARPA’s TERN program.
Single-aisle commercial transport development was incredibly active. The A320neo, with Connecticut-based Pratt & Whitney engines, was delivered to Lufthansa on Jan. 20. Boeing’s first flight of the 737 MAX was Jan. 29. The A321neo’s first flight, powered by CFM engines, was Feb. 9. Embraer rolled out its first E-Jet E2, an E190-E2, in February. The Pratt & Whitney geared turbofan-powered aircraft had its inaugural flight in late May. The Russian Irkut MS-21-300 variant rolled out in June. Comac’s ARJ21 entered service in June with Chengdu Airlines. Bombardier’s C Series also entered service, with the CS100 variant delivered to Swiss Global Air Lines in July. Its larger sibling, the CS300, obtained Transport Canada certification the same month.
In General Aviation, Austria’s Diamond Aircraft Industries flew its DART-450 Turboprop on May 17. Tecnam’s P2012 Traveler’s first flight was July 21. The Cessna Citation Longitude, a super-midsized business jet, first flew in October.
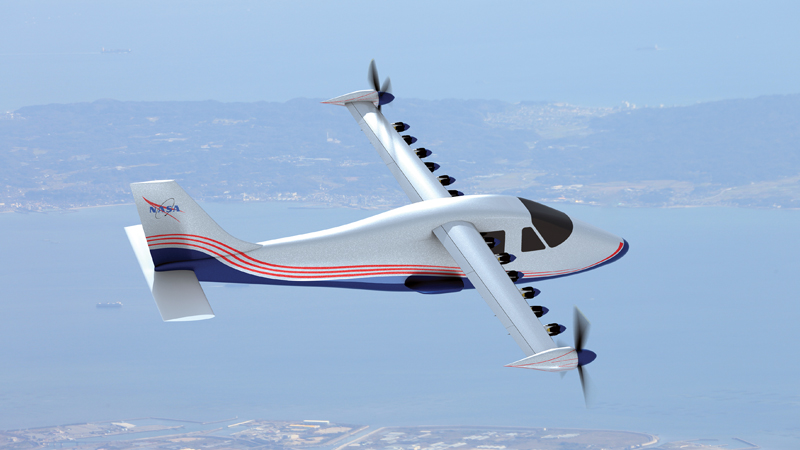
In civil research, NASA reported the results of its multiyear Environmentally Responsible Aviation Project, aimed at advancing technologies for more efficient commercial transports. A wide variety of technologies and concepts were examined indicating that substantial advancements in fuel efficiency, lower carbon dioxide and oxides of nitrogen emissions, and improved community noise are all feasible. With this, NASA began shifting focus on developing X-planes to further technology readiness. Its X-57 Maxwell, under the Scalable Convergent Electric Propulsion Technology and Operations Research, or SCEPTOR, program, is a manned, electrically powered, multiple propeller wing aircraft. NASA moved forward with its Quiet Supersonic Technology low-boom flight demonstrator with an award to Lockheed Martin’s Skunk Works. NASA granted additional X-plane development contracts to support concept development for its Ultra Efficient Subsonic Transport Thrust.
Advancements in electric-based propulsion aircraft abounded. Switzerland’s Solar Impulse 2 completed its 16-month round-the-world circumnavigation by an all-electric manned vehicle, upon landing in Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates, in July. NASA, along with SCEPTOR, also explored hybrid electric propulsion concept work. In April, Airbus and Siemens announced they signed a cooperation agreement to develop prototypes of hybrid-electric propulsion systems for future commercial transports. Among many small electric vehicles in development, Germany’s E-Volo VC200 multicopter, a two-seat VTOL, had its inaugural flight in March. The FAA’s new Part 107 for unmanned aircraft under 55 pounds (about 25 kilograms), is expected to unleash a proliferation of vehicle design, electric or otherwise, in this rapidly developing market niche. ★